When selecting server hosting services, VPS (Virtual Private Server) and VDS (Virtual Dedicated Server) are two frequently mentioned options. Whether you are a small business owner or a technical expert in a large enterprise, understanding the differences between these two types of servers is crucial for making the best decision. Both VPS and VDS have their unique advantages and suitable use cases, but their distinctions can often be confusing. This article will delve into the characteristics, applications, and key differences between VPS and VDS, helping you choose the option that best fits your needs.
What is a Virtual Private Server (VPS)?
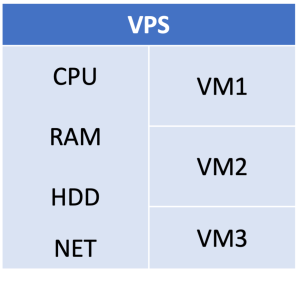
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a hosting service that uses virtualization technology to simulate a dedicated server environment within a shared server. The virtualization layer used in VPS typically operates at the operating system level, with popular technologies like OpenVZ based on the Linux Kernel. VPS provides scalability, allowing users to start with limited resources and expand as their needs grow.
VPS Key Features:
- Shared but isolated environment: Users share the physical server but enjoy isolated virtual environments.
- Scalability: Resources can be adjusted based on demand.
- Cost-efficient: Ideal for businesses with a smaller budget or individual projects.
What is a Virtual Dedicated Server (VDS)?
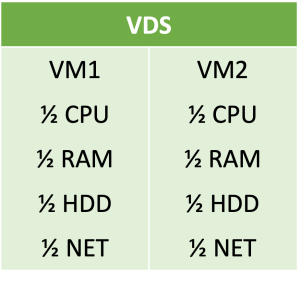
A Virtual Dedicated Server (VDS) is a virtual machine that allows users to rent a managed but dedicated server for hosting websites and applications. Unlike VPS, a VDS is not shared with other customers and does not operate in a multi-tenant environment. Each VDS has its own disk space, CPU configuration, memory, bandwidth, and operating system, typically relying on Hypervisor technology to create logical partitions. VDS offers dedicated resources exclusively for a single client, without the need to share them with others.
VDS Key Features:
- Dedicated resources: Ensures consistent performance with no interference from other tenants.
- High reliability: Designed for demanding workloads or high-traffic applications.
- Customizability: Complete control over server configuration.
The Main Difference between VPS and VDS
|
Comparison Item |
VPS |
VDS |
|
Naming Difference |
Created at the operating system level using virtualization; commonly referred to as VPS. |
Created using semi-hardware-level virtualization, referred to as VDS. |
|
Execution Volume |
VPS shares a physical server, running multiple virtual servers simultaneously. |
VDS occupies an entire physical server for a single instance. |
|
Cost Efficiency |
VPS is more cost-effective than VDS. |
VDS is generally less cost-efficient. |
|
Scalability |
VPS usually provides certain scalability and flexibility. |
VDS does not offer scalability or flexibility. |
|
Technical Advantage |
VPS utilizes OpenVZ technology, which relies on the operating system’s virtualization, focusing on speed. |
VDS uses KVM technology, allowing users to install operating systems and use VNC for full server control as if using physical hardware. |
|
Features |
VPS offers fewer features than VDS. |
VDS provides more advanced features than VPS. |
|
Management and Control |
VPS is controlled at the operating system level. |
VDS is managed at the hardware level. |
|
Server Environment |
VPS provides a shared environment where users have their allocated virtual space but still share physical resources with others. |
VDS provides a dedicated environment where all resources are exclusive to one user. |
|
Suitable Use Cases |
Ideal for lightweight workloads such as hosting websites, small e-commerce platforms, and enterprise applications. |
Suitable for high-traffic applications, gaming servers, high-demand environments, and large e-commerce platforms. |
How to Choose the Right Server?
Your choice between VPS and VDS depends primarily on your requirements and budget:
- VPS: If your application workload is relatively low and you want a cost-effective solution with some scalability, VPS is an ideal choice. It’s suitable for small business websites, development and testing environments, or personal projects.
- VDS: If you need higher performance and dedicated resources, and your application handles large amounts of traffic or data, such as streaming, gaming servers, or large e-commerce websites, then VDS may be a better fit. Although it comes with a higher cost, it provides greater functionality and reliability.
VPS Recommendations
VPS is a flexible and affordable solution for efficient resource management and application deployment. BigBull Technology offers VPS solutions from top providers such as AWS, GCP, Alibaba Cloud, and Tencent Cloud, ensuring high-performance VPS to meet diverse customer needs.
Advantages of Choosing BigBull Technology
- Multiple Payment Options: Supports cryptocurrency, USDT, credit cards, and Apple Pay.
- Global Coverage: Services available in up to 50 regions with low-latency access.
- Trusted by 2,000+ Clients: Demonstrating reliable and trustworthy services.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go pricing for controlled expenses.
- Security and Stability: Partners with top cloud providers for enhanced reliability.
- User-Friendly Interface: Simplified AWS and GCP solutions for easy use without the complexities.
By understanding the differences between VPS and VDS, you can choose the optimal solution for your unique requirements, leveraging BigBull Technology’s expertise and services to enhance your hosting experience.
Learn more about how VPS Solutions Empower Your Business in the Digital Cloud